Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry
Basic Concept of Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry:
The Branch of chemistry which deals with the organic
compound is called Organic Chemistry.
Organic
Compound:
Those compound which are obtained from living organism were
called as organic compound. Example: Sugar, urea.
Or
Those compound which were developed from hydrocarbon and
their derivative is called Organic compound.
Vital
Force Theory:
Organic compounds can only be prepared or obtained by mysterious
force existed in living beings". Accordingly, synthesis in lab was considered
to be impossible.
In 1828 Friedrich Wohler made discovery which include the
production of urea (organic compound) in the lab by heating ammonia and cyanic
acid.
NH3 + HCNO
→NH4CNO
NH4CNO→CO(NH2)2
Note: First
synthesized organic compound CH3-COOH (Acetic acid by Kolbe).
Modern
definition of organic compounds:-
"Hydrocarbons & their derivatives with covalently
bonded carbon as essential element."
"Compounds of carbon except CO, CO2,
carbonates bicarbonates, carbides, some cyanides etc."
Organic Chemistry→ Study of chemistry of organic compounds.
Tetra-valency
and Catenation Property of Carbon:
i.
Tetravalencey:
Carbon consists four valance electron in its outermost shell and shows
tetravalencey. Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing valance electron is
called tetravalencey of carbon.
ii.
Catenation:
Self-linking property exhibited by carbon to result long chain, branched chain
& cyclic form, It is due to strong sharing tendency by its optimum
electronegativity and smaller size.
Example: CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3
Classification
of Organic Compound:

Aliphatic
Hydrocarbon: The
hydrocarbon which have straight chain carbon to carbon linkage is called
aliphatic hydrocarbon.
i.
Alkane:
Hydrocarbon with single bond between carbons are called alkane.
Example: Methane (CH3-CH3)
ii.
Alkene:
Hydrocarbon with double bond between carbons are called alkane.
Example: Ethene (CH2=CH2)
iii.
Alkyne:
Hydrocarbon with triple bond between carbons are called alkane.
Example: Ethyne (CH≡CH2)
Cyclic or Closed chain Hydrocarbon: Those
hydrocarbon in which carbon to carbon linkage is present in the form of circle
or ring are called Cyclic or Closed chain Hydrocarbon.
i.
Homo-cyclic
Hydrocarbon: Those cyclic hydrocarbon in which ring atom are only carbon
are called homo-cyclic hydrocarbon.
a.
Alicyclic:
The cyclic organic compound which are similar to open chain compound in chemical
behavior are called alicyclic or cyclic aliphatic organic compound.
Example: Cyclohexene
a.
Aromatic:
Benzene and benzene like organic compounds are called aromatic compound.
Example: Phenol
i.
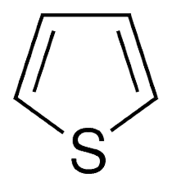
Heterocyclic
Compounds: The cyclic organic compounds which contains a skeleton of a
cyclic ring containing at least a heteroatom in addition to carbon atom are
called heterocyclic compound.
Example:
Thiophene
Alkyl Group:
A group which is obtained by removing a hydrogen atom from alkane are called alkyl group.
Note: Remaining Note will be uploaded Soon!!